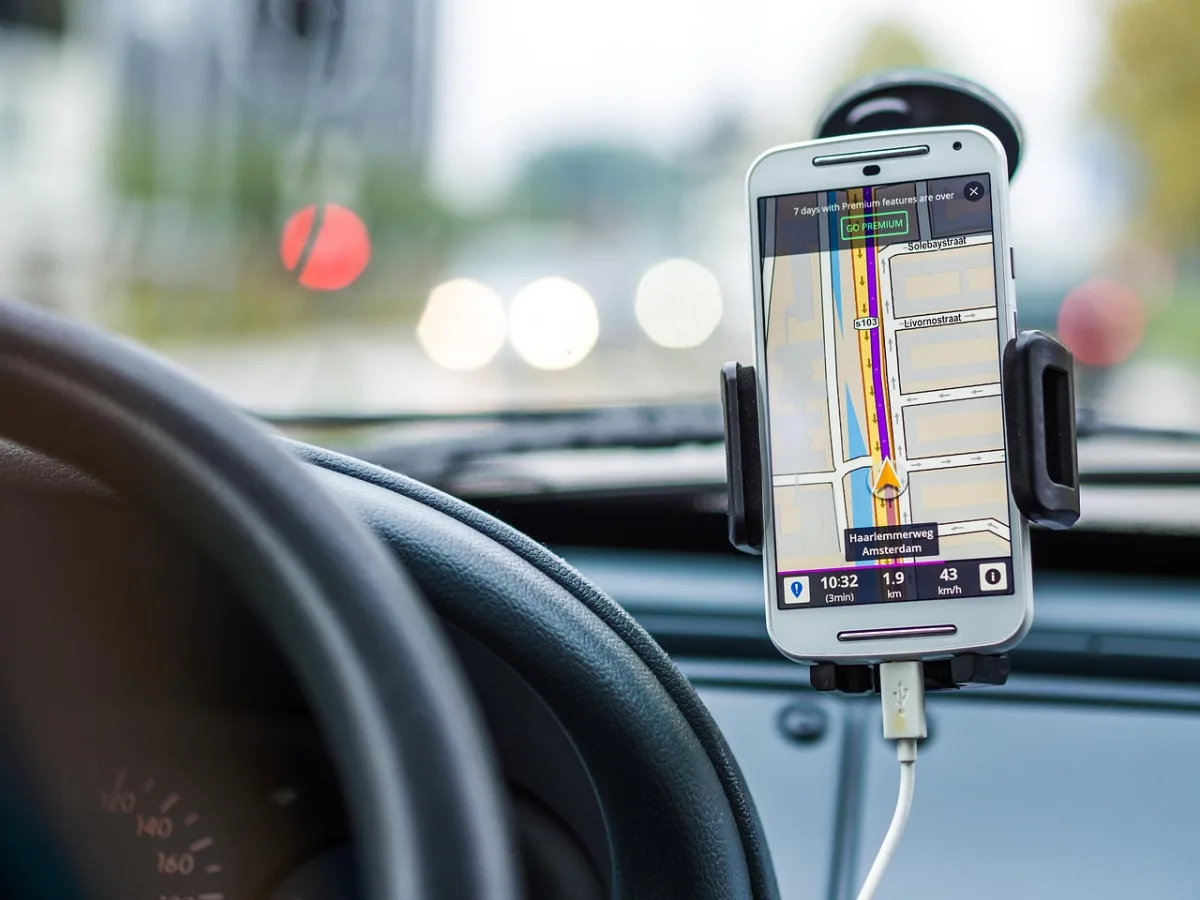
Have you ever walked into a store and received a push notification with a special offer or discount on your phone? You’re not alone. Many of us have experienced this phenomenon, and it’s all thanks to location-based mobile apps that utilize geofencing, beacons, and location services to deliver personalized experiences.
As someone who’s worked with these technologies, I can attest to their power in transforming the way businesses interact with their customers. By understanding how to effectively use location-based services, you can create engaging experiences that drive loyalty and revenue.
In your daily life, you likely encounter location-based apps without even realizing it – from social media check-ins to fitness tracking. But have you ever stopped to think about the technology behind these experiences? By exploring the ins and outs of location-based mobile apps, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how to harness their potential for your own purposes.
As we explore the world of location-based mobile apps, you’ll discover the practical applications and benefits of geofencing, beacons, and location services, and learn how to apply these technologies to your own projects and business ventures, ultimately enhancing your ability to connect with your audience and drive results.
Introduction to Location-Based Mobile Apps
I still remember the first time I used a location-based mobile app – it was a restaurant finder that used my phone’s GPS to suggest nearby eateries. I was impressed by how accurately it pinpointed my location and provided relevant results. Since then, location-based mobile apps have become an integral part of our daily lives. You can use them to find the nearest coffee shop, get directions to a meeting, or even receive exclusive offers from stores you’re walking by.

So, what exactly are location-based mobile apps? Simply put, they are apps that use geolocation technologies like GPS, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks to provide location-specific services or information. These apps can be categorized into various types, including navigation apps, social apps, and marketing apps. According to a recent survey, over 70% of smartphone users use location-based services at least once a week, highlighting the significance of these apps in our daily routines.
Statistics and Trends
The popularity of location-based mobile apps is evident from the statistics. For instance, the number of location-based service users is expected to reach 1.5 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 25%. A case study of the coffee shop chain, Starbucks, is a great example of how location-based marketing can be effective. By using location-based targeting, Starbucks was able to increase sales by 25% and boost customer engagement by 50%. You can use location-based apps to achieve similar results, whether you’re a business owner or a developer looking to create the next big app.
As you consider developing or using location-based mobile apps, you might wonder what makes them so effective. The answer lies in their ability to provide context-aware services that are relevant to the user’s current location. By combining location data with other factors like time, weather, and user preferences, these apps can offer a highly personalized experience that enhances the user’s interaction with the physical world. With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and artificial intelligence, the potential of location-based mobile apps is vast and exciting, and we’re only just beginning to explore their possibilities.
Geofencing and Its Applications
I still remember the first time I received a push notification from a coffee shop I was walking by, offering me a discount on my favorite latte. This was my introduction to geofencing, a technology that allows apps to trigger actions based on a device’s proximity to a specific location. As I dug deeper, I realized the potential of geofencing extends far beyond marketing and advertising.

Geofencing is essentially a virtual fence around a physical location, which can be a point of interest, a building, or even a room. When a device enters or exits this fenced area, the app can trigger a specific action, such as sending a notification, activating a feature, or collecting data. You can use geofencing to create personalized experiences, improve customer engagement, and even enhance operational efficiency.
Practical Uses of Geofencing
One of the most significant advantages of geofencing is its ability to provide context-aware experiences. For instance, a museum can use geofencing to offer visitors interactive guides and information about the exhibits they are standing in front of. Similarly, a retailer can use geofencing to send customers special offers and discounts when they are near a specific product or department. You can also use geofencing to track employee movements, monitor asset locations, and even optimize logistics and supply chain operations.
A great example of geofencing in action is the Domino’s Pizza app, which allows customers to track their orders and receive notifications when their pizza is ready for pickup. The app uses geofencing to detect when the customer is near the store, and sends them a notification to let them know their order is ready. This not only improves the customer experience but also helps the store staff to manage pickups more efficiently.
As you can see, geofencing has a wide range of applications, from marketing and advertising to operations and logistics. By understanding how geofencing works and how to use it effectively, you can create innovative and engaging experiences for your customers, and even gain a competitive edge in your industry. You can use geofencing to collect valuable data about customer behavior, improve customer satisfaction, and increase sales. With the right strategy and implementation, geofencing can be a powerful tool in your mobile app arsenal.
Beacons and Proximity Marketing
I still remember the first time I walked into a store and received a personalized offer on my phone. I was at a coffee shop, and as I waited in line, my phone buzzed with a notification – a discount on my favorite coffee drink. This was my introduction to beacons and proximity marketing. Here’s what really matters though: understanding how beacons work and their role in creating personalized experiences for customers.

A beacon is essentially a small device that transmits a unique identifier to nearby devices, typically using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology. This identifier can trigger a specific action on a mobile device, such as sending a notification or displaying a message. Proximity marketing, on the other hand, refers to the practice of targeting customers with relevant content and offers based on their physical location. When combined, beacons and proximity marketing can create powerful experiences that drive engagement and sales.
For example, a retailer like Macy’s can use beacons to send personalized offers to customers as they walk into a store. Let’s say a customer has a history of buying clothing from a specific brand – the beacon can trigger a notification with a discount on that brand’s latest collection. This not only enhances the customer’s shopping experience but also increases the chances of a sale. You can also use beacons to provide customers with helpful information, such as store maps or product reviews, to make their shopping experience more enjoyable.
One specific example that comes to mind is the Shopkick app, which uses beacons to reward customers for walking into stores and engaging with products. The app can detect when a customer is near a specific product and offer rewards or discounts in real-time. This approach has been shown to increase foot traffic and sales for participating retailers. As you consider implementing beacons and proximity marketing in your own business, think about how you can use these technologies to create meaningful interactions with your customers.
Location Services and GPS Technology
I still remember my first experience with a location-based mobile app – I was trying to find the nearest coffee shop in an unfamiliar city. As I opened the app, it prompted me to enable location services, and suddenly, a list of nearby cafes appeared on my screen. But here’s where it gets interesting – have you ever stopped to think about the technology behind this seamless experience? Location services, which enable apps to determine your device’s location, rely heavily on GPS technology. GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, providing location information to GPS receivers on the ground.

Location services definition is quite straightforward – it refers to the ability of a mobile device to determine its location and provide that information to applications. This is achieved through a combination of GPS, cell tower triangulation, and Wi-Fi positioning. As a result, location services have a wide range of applications, from mapping and navigation to social media and advertising. For instance, Foursquare, a popular social media app, uses location services to help users discover new places and share their experiences with friends. You can use location services to get directions, find nearby points of interest, or even receive targeted ads based on your location.
A great example of location services in action is the Waze traffic app, which relies on user-generated data to provide real-time traffic updates. By using GPS technology to determine the location of its users, Waze can provide accurate and up-to-date information on traffic conditions, helping users avoid congested roads and reduce their commute time. You can also use location services to create custom apps, such as a fitness app that tracks your runs or a travel app that provides location-based recommendations. As you explore the possibilities of location services, you start to appreciate the complexity and nuance of this technology – and the many ways it can be used to create innovative and user-friendly apps.
As I reflect on my experience with location-based mobile apps, I’m struck by the potential of this technology to transform the way we interact with our surroundings. With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, location services will play an increasingly important role in enabling smart cities, smart homes, and other connected environments. You can already see this trend in action, with companies like Uber and Lyft using location services to provide on-demand transportation services. As location services continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of this technology – and new opportunities for developers to create apps that change the way we live and work.
Benefits and Challenges of Location-Based Mobile Apps
I still remember my first experience with a location-based mobile app – a coffee shop finder that used my phone’s GPS to locate the nearest cafe. I was amazed by how easily I could find a great cup of coffee, no matter where I was in the city. This was just the beginning of my journey into the world of location-based mobile apps, and I’ve since seen the technology evolve to include features like geofencing and beacons.

One of the main benefits of location-based mobile apps is the ability to provide users with hyper-local information and offers. For example, a retail app can use geofencing to send a push notification to a user when they’re near a store, offering them a discount on a specific product. This can be a powerful marketing tool, as it allows businesses to target users who are already in the vicinity of their store. A case study by Shopkick found that users who received location-based offers were more likely to make a purchase than those who didn’t.
Despite the benefits, there are also significant challenges associated with location-based mobile apps. One of the main challenges is ensuring that the app’s location services are accurate and reliable. This requires a deep understanding of locationing technologies like GPS, Wi-Fi, and cell ID. You can use frameworks like Core Location to build location-based features into your app, but you’ll still need to test and refine your app to ensure that it works as expected. As I’ve seen in my own experience, a well-designed location-based app can be a powerful tool for businesses and users alike – but a poorly designed app can be frustrating and even alienating.
So what does the future hold for location-based mobile apps? As locationing technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and accurate location-based features. For instance, beacon technology is already being used in airports and museums to provide users with detailed information about their surroundings. As these technologies become more widespread, we can expect to see a wide range of new and innovative location-based apps – and I’m excited to see what the future holds.
Best Practices for Developing Location-Based Mobile Apps
I recall working on a project for a retail client who wanted to create a location-based mobile app that would send personalized offers to customers when they walked into their stores. As we began development, we realized that a one-size-fits-all approach wouldn’t work. Different stores had varying layouts, and the app needed to account for these nuances. This experience taught me that developing location-based mobile apps requires careful consideration of multiple factors.

When building a location-based app, you must consider development considerations such as the type of location technology to use (e.g., geofencing, beacons, or GPS), the level of precision required, and the impact of battery life on the user experience. For instance, if your app relies on continuous location tracking, you’ll need to implement strategies to minimize battery drain, such as using deferred location updates or activity-based location tracking. You can also use design principles like simplicity and clarity to ensure that your app’s location-based features are intuitive and easy to use.
Design and Testing Strategies
A well-designed location-based app should provide a clear value proposition to the user, such as offering rewards, discounts, or exclusive content. To achieve this, you can use user-centered design methodologies, like creating personas and user journeys, to understand how your target audience will interact with your app. When testing your app, you should use a combination of unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing to ensure that your location-based features work as expected. For example, you can create a testing matrix that outlines different scenarios, such as varying locations, network conditions, and device types, to validate your app’s performance and accuracy.
One specific example that comes to mind is the Starbucks app, which uses location-based technology to offer customers personalized promotions and rewards when they’re near a store. The app’s design is simple and intuitive, making it easy for users to understand and engage with the location-based features. By following best practices like these, you can create a location-based mobile app that provides a compelling and effective user experience.
Empowering Your Mobile Presence
Imagine walking into your favorite coffee shop and receiving a personalized offer on your phone, making your day a little brighter. This is the power of location-based mobile apps. By understanding how geofencing, beacons, and location services work together, you can create engaging experiences for your customers. The key to success lies in crafting an app that intuitively responds to users’ physical surroundings, providing value that feels tailored to their needs. What will you create when you start developing your own location-based mobile app today?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is geofencing?
Geofencing is a technology that uses GPS or RFID to define a virtual boundary around a physical location
How do beacons work?
Beacons use Bluetooth Low Energy technology to transmit signals to nearby devices